Wed, Sep 3, 2025
| فارسی
Volume 23, Issue 4 (Winter 2018)
IJPCP 2018, 23(4): 424-437 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Hosseinzadeh Firouzabad Y, Bassak Nejad S, Davoudi I. Prediction of Subscale Test Anxiety Considering Behavioral Procrastination, Decisional Procrastination and Cognitive Avoidance in University Students. IJPCP 2018; 23 (4) :424-437
URL: http://ijpcp.iums.ac.ir/article-1-2573-en.html
URL: http://ijpcp.iums.ac.ir/article-1-2573-en.html
1- Faculty of Education and Psychology, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran , E-mail: hosseinzadeh.yahya@gmail.com
2- Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Education and Psychology, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran
3- , Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Education and Psychology, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran
2- Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Education and Psychology, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran
3- , Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Education and Psychology, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran
Full-Text [PDF 3059 kb]
(4998 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (10525 Views)
Full-Text: (8913 Views)
Extended Abstract
1. Introduction
Anxiety, as a part of every person’s life, is considered as an appropriate and consistent response. Lack of anxiety or excessive anxiety can lead to significant problems and dangers. In this research, the relationship between behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination, and cognitive avoidance with subscales test anxiety (Derogation, Obstruction, and Tenseness) have been investigated.
Empirical research has shown that anxiety is positively related to procrastination and plays a role in its formation. By eliminating the anxiety agent (evaluation position), the amount of procrastination in procrastinators is reduced [12]. Studies have showed that procrastination is associated with certain concerns such as fear of failure, test anxiety, social anxiety, and shyness [13]. Various research findings suggest that selecting one of the coping styles or combinations of them can help survive and face mental pressures. Meanwhile, avoidance coping is trying to avoid negative events, which can be manifested cognitively and behaviorally [19].
Most of the researchers, especially in the Iranian society, have not paid adequate attention to other aspects of procrastination (such as behavioral procrastination and decisional procrastination) and have considered cognitive avoidance with social anxiety. Therefore, by considering the effect of procrastination and cognitive avoidance in creating anxiety, this research attempts to determine whether behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination, and cognitive avoidance are related to subscales test anxiety among students.
2. Method
The research method is a canonical correlation, which is the relationship between two variables, one of which is derived from the linear combination of independent variables and the other from the combination of dependent variables. The statistical population of this study included all male and female students studying in the academic year of 2015–2016 in the Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz. In this research, multi-stage cluster sampling method was used to select 200 students for testing the hypotheses. In this way, five faculties were randomly selected; from each faculty, several classes were selected, and in each class, several students were selected to answer the questionnaires. For data collection, we used the General Procrastination scale, Decisional Procrastination scale, cognitive avoidance questionnaire, and Fried-Ben test anxiety questionnaire. The reliability of the scale was obtained using Cronbach’s alpha.
Data analysis was carried out using the SPSS-17 software. In order to analyze the research hypotheses, parametric statistical methods were used. The canonical correlation analysis was used to study the prediction of a linear combination of criterion variables by a linear combination of predictor variables. The multivariate regressions analysis was conducted to study the multiple relationships between predictor variables with each of the criterion variables.
3. Results
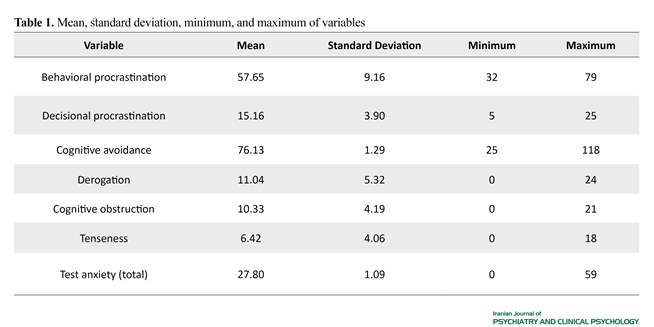
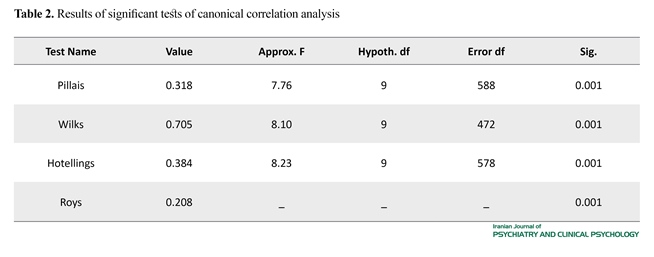
The demographic information of the sample is shown in Table 1. The results of significant tests of canonical correlation analysis full model are presented in Table 2. As seen in Table 2, Wilks’s Lambda (P<0.001, λ=0.705, F=8.10) indicate that there is a significant relationship between the two categories variables (behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination and cognitive avoidance with derogation, obstruction, and tenseness). Regarding the full model significance, the first hypothesis of the current study (prediction of subscale test anxiety considering predictor variables) is confirmed. Therefore, the model obtained in this study determines 29.5% of the variance between behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination and cognitive avoidance (as a predictor variable) variables with derogation, obstruction, and tenseness (as a criterion variable).
The results of multivariate regression analysis showed that behavioral procrastination and decisional procrastination significantly predicted derogation (β=0.302, P<0.001 and β=0.238, P<0.001) and obstruction (β=0.381, P<0.001 and β=0.204, P<0.006) in students. Also, behavioral procrastination and cognitive avoidance predicted tenseness (β=0.314, P<0.001 and β=0.246, P<0.002) in students.
4. Discussion
The results of the study showed that there is a significant relationship between the canonical predictor variables as behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination and cognitive avoidance with the canonical criterion variables. In other words, these variables predict subscales test anxiety. Due to negligence, most of the students delay studying their lessons until the night of the exam. This results in anxiety before the exam [37], leading to academic failure. As a result, the students feel that they do not have the necessary qualifications, and their academic confidence is seriously damaged. According to Onwuegbuzie’s hypothesis [38], anxiety and procrastination are in a two-way relationship and interact in a complicated way; hence, negligent students experience high levels of anxiety due to the feeling of threat to their self-esteem. High levels of anxiety postpone the probability of doing that task, to relieve the resulting suffering.
As stated previously, cognitive avoidance, as one of the predictor variables, can predict test anxiety. This result can be explained by the Lazarus and Folkman theories. These theorists believed that the person in the situation of stress or task first assesses his/her ability and the difficulty and threats of the task. If, based on this assessment, the situation is disturbing or unpleasant for a person, he or she experiences a negative emotion such as anxiety. Here, the person uses coping styles such as avoiding the situation to escape from anxiety. Therefore, the person who has test try to avoid situations and thoughts related to test that can also delay the doing of the task.
1. Introduction
Anxiety, as a part of every person’s life, is considered as an appropriate and consistent response. Lack of anxiety or excessive anxiety can lead to significant problems and dangers. In this research, the relationship between behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination, and cognitive avoidance with subscales test anxiety (Derogation, Obstruction, and Tenseness) have been investigated.
Empirical research has shown that anxiety is positively related to procrastination and plays a role in its formation. By eliminating the anxiety agent (evaluation position), the amount of procrastination in procrastinators is reduced [12]. Studies have showed that procrastination is associated with certain concerns such as fear of failure, test anxiety, social anxiety, and shyness [13]. Various research findings suggest that selecting one of the coping styles or combinations of them can help survive and face mental pressures. Meanwhile, avoidance coping is trying to avoid negative events, which can be manifested cognitively and behaviorally [19].
Most of the researchers, especially in the Iranian society, have not paid adequate attention to other aspects of procrastination (such as behavioral procrastination and decisional procrastination) and have considered cognitive avoidance with social anxiety. Therefore, by considering the effect of procrastination and cognitive avoidance in creating anxiety, this research attempts to determine whether behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination, and cognitive avoidance are related to subscales test anxiety among students.
2. Method
The research method is a canonical correlation, which is the relationship between two variables, one of which is derived from the linear combination of independent variables and the other from the combination of dependent variables. The statistical population of this study included all male and female students studying in the academic year of 2015–2016 in the Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz. In this research, multi-stage cluster sampling method was used to select 200 students for testing the hypotheses. In this way, five faculties were randomly selected; from each faculty, several classes were selected, and in each class, several students were selected to answer the questionnaires. For data collection, we used the General Procrastination scale, Decisional Procrastination scale, cognitive avoidance questionnaire, and Fried-Ben test anxiety questionnaire. The reliability of the scale was obtained using Cronbach’s alpha.
Data analysis was carried out using the SPSS-17 software. In order to analyze the research hypotheses, parametric statistical methods were used. The canonical correlation analysis was used to study the prediction of a linear combination of criterion variables by a linear combination of predictor variables. The multivariate regressions analysis was conducted to study the multiple relationships between predictor variables with each of the criterion variables.
3. Results
The demographic information of the sample is shown in Table 1. The results of significant tests of canonical correlation analysis full model are presented in Table 2. As seen in Table 2, Wilks’s Lambda (P<0.001, λ=0.705, F=8.10) indicate that there is a significant relationship between the two categories variables (behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination and cognitive avoidance with derogation, obstruction, and tenseness). Regarding the full model significance, the first hypothesis of the current study (prediction of subscale test anxiety considering predictor variables) is confirmed. Therefore, the model obtained in this study determines 29.5% of the variance between behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination and cognitive avoidance (as a predictor variable) variables with derogation, obstruction, and tenseness (as a criterion variable).
The results of multivariate regression analysis showed that behavioral procrastination and decisional procrastination significantly predicted derogation (β=0.302, P<0.001 and β=0.238, P<0.001) and obstruction (β=0.381, P<0.001 and β=0.204, P<0.006) in students. Also, behavioral procrastination and cognitive avoidance predicted tenseness (β=0.314, P<0.001 and β=0.246, P<0.002) in students.
4. Discussion
The results of the study showed that there is a significant relationship between the canonical predictor variables as behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination and cognitive avoidance with the canonical criterion variables. In other words, these variables predict subscales test anxiety. Due to negligence, most of the students delay studying their lessons until the night of the exam. This results in anxiety before the exam [37], leading to academic failure. As a result, the students feel that they do not have the necessary qualifications, and their academic confidence is seriously damaged. According to Onwuegbuzie’s hypothesis [38], anxiety and procrastination are in a two-way relationship and interact in a complicated way; hence, negligent students experience high levels of anxiety due to the feeling of threat to their self-esteem. High levels of anxiety postpone the probability of doing that task, to relieve the resulting suffering.
As stated previously, cognitive avoidance, as one of the predictor variables, can predict test anxiety. This result can be explained by the Lazarus and Folkman theories. These theorists believed that the person in the situation of stress or task first assesses his/her ability and the difficulty and threats of the task. If, based on this assessment, the situation is disturbing or unpleasant for a person, he or she experiences a negative emotion such as anxiety. Here, the person uses coping styles such as avoiding the situation to escape from anxiety. Therefore, the person who has test try to avoid situations and thoughts related to test that can also delay the doing of the task.
In summary, the results of the current study show that the people with behavioral procrastination, decisional procrastination, and cognitive avoidance experience more test anxiety and experience the fear of humiliation, irrational and negative thoughts, and more tenseness. In the end, it can be said that the lack of proper planning, lack of specific goals, and lack of proper problem-solving strategies, which refer to procrastination and avoidance characteristics, can increase anxiety. The limitations of this research include the mental state of the person at the time of completion of the questionnaire, time-consuming and honesty in responding, which is a basic condition of health and accuracy of research. Given that many students experience anxiety in a particular lesson, the anxiety of a particular lesson can be the subject of future research.
Acknowledgments
This research was extracted from the MSc. thesis of the first author in the Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, Shahid Chamran University of Ahwaz, Ahwaz, Iran.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This research was extracted from the MSc. thesis of the first author in the Department of Clinical Psychology, Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, Shahid Chamran University of Ahwaz, Ahwaz, Iran.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
References
[1]Abolghasemi A, Najarian B. [Test anxiety, assessment and treatment (Persian)]. Psychological Research. 2000; 5(3-4):82-99.
[2]Latas M, Pantic M, Bradovic D. Analysis of test anxiety in medical students. Medicinski Pregled. 2010; 63(11-12):863-6. doi: 10.2298/mpns1012863l
[3]Brown LA, Forman EM, Herbert JD, Hoffman KL, Goetter EM. A randomized Controlled trial of acceptance-based behavior therapy and cognitive therapy for test anxiety: A pilot Study. Behavioural Modification. 2011; 35(1):31-53. doi: 10.1177/0145445510390930
[4]Schaefer A, Matthess H, Pfitzer G, Kohle K. [Mental health and performance of medical students with high and low test anxiety (German)]. PPmP - Psychotherapie · Psychosomatik · Medizinische Psychologie. 2007; 57(7):289-97. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-951974
[5]Pless A. Treatment of test anxiety: A computerized approach [PhD dissertation]. Michigan: Centeral Michigan University; 2010.
[6]Morris LW, Liebert RM. Effects of anxiety on timed and untimed intelligence tests: Another look. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1969; 33(2):240–4. doi: 10.1037/h0027164
[7]Spilberger CD. Preliminary professional manual for the Test Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, California: Consulting Psychologist Press; 1980.
[8]Nasri S, Shahrokhi M, Ebrahim Damavandi M. [The prediction of academic procrastination on perfectionism and test anxiety (Persian)]. Research in School and Virtual Learning. 2013; 1(1):26-37.
[9]Howell AJ, Watson DC. Procrastination: Associations with achievement goal orientation and learning strategies. Personality and Individual Differences. 2007; 43(1):167–78. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2006.11.017
[10]Kim KR, Seo EH. The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: A meta-analysis. Personality and Individual Differences. 2015; 82:26–33. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.02.038
[11]Ferrari JR, Ozer BU, Demir A. Chronic procrastination among Turkish adults: Exploring decisional, avoidant, and arousal styles. The Journal of Social Psychology. 2009; 149(3):302-08. doi: 10.3200/socp.149.3.302-308
[12]Sheykhi M, Fathabadi J, Heidari M. [The relations of anxiety, self-efficacy and perfectionism to dissertation procrastination (Persian)]. Developmental Psychology. 2013; 9(35):283-95.
[13]Solomon LJ, Rothblum ED. Academic procrastination: Frequency and cognitive behavioural correlates. Journal of Counselling Psychology. 1984; 31(4):503-9. doi: 10.1037//0022-0167.31.4.503
[14]Soysa CK, Weiss A. Mediating perceived parenting styles–test anxiety relationships: Academic procrastination and maladaptive perfectionism. Learning and Individual Differences. 2014; 34:77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2014.05.004
[15]Putwain D, Symes W. Perceived fear appeals and examination performance: Facilitating or debilitating outcomes? Learning and Individual Differences. 2011; 21(2):227–32. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2010.11.022
[16]Ferrari JR, Dovidio JF. Examining behavioral processes in indecision: Decisional Procrastination and decision- making style. Journal of Research in Personality. 2000; 34(1):127–37. doi: 10.1006/jrpe.1999.2247
[17]Walsh JJ, Ugumba-Agwunobi G. Individual differences in statistics anxiety: The roles of perfectionism, procrastination and trait anxiety. Personality and Individual Differences. 2002; 33(2):239–51. doi: 10.1016/s0191-8869(01)00148-9
[18]Gosselin P, Langlois F, Freeston MH, Ladouceur R, Laberge M, Lemay D. Cognitive variables related to worry among adolescents: Avoidance strategies and faulty beliefs about worry. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2007; 45(2):225–33. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2006.03.001
[19]Bassak-nejad S, Hooman F, Ghasemi-nejad MA. [The relationship between cognitive-behavioral avoidance coping styles with eating disorder among university students (Persian)]. Journal of Fundamentals of Mental Health. 2013; 14(56):278-85.
[20]Beesdo-Baum K, Jenjahn E, Höfler M, Lueken U, Becker ES, Hoyer J. Avoidance, safety behavior, and reassurance seeking in generalized anxiety disorder. Depression and Anxiety. 2012; 29(11):948‒57. doi: 10.1002/da.21955
[21]Moini N. [A study of relationship between post event processing and cognitive avoidance with social anxiety among students of Shahid Chamran university of Ahwaz (Persian)] [MSc. thesis]. Ahwaz: Shahid Chamran University of Ahwaz; 2010.
[22]Bassak Nejad S. The relationship between cognitive avoidance and pathological worry among university students. Paper presente at: 23rd Conference of EHPS. 15-19 September 2009; Pisa, Italy.
[23]Dickson KS, Ciesla JA. Reilly LC. Rumination, worry, cognitive avoidance, and behavioral avoidance: Examination of temporal effects. Behavior Therapy. 2012; 43(3):629–40. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2011.11.002
[24]Sexton, KA. Dugas MJ. The cognitive avoidance questionare: Vlidetion of the English translation. Journal of Anxiety Disorder. 2008; 22(3):355–70. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.04.005
[25]Gosselin P, Langlois F, Freeston MH, Ladouceur R, Dugas MJ, Pelletier O. [The Cognitive Avoidance Questionnaire(CAQ): Development and validation among adult and adolescent samples (French)]. Journal de The´rapie Comportementale et Cognitive 2002; 12(1):24–37.
[26]Bassak-nejad S, Moini N, Mehrabizadeh-Honarmand M. [The relationship between post event processing and cognitive avoidance with social anxiety among students (Persian)]. International Journal of Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 4(4): 335-40.
[27]Fridman I, Bendas-Jacob O. Measuring precieved test anxiety inadolescents: A self-report scale. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 1997; 57(6):1035–46. doi: 10.1177/0013164497057006012
[28]Lay CH. At last, my research article on procrastination. Journal of Research in Personality. 1986; 20(4):474–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-6566(86)90127-3
[29]Ferrari JR. Reliability of academic and dispositional measure of procrastination. Psychological Reports. 1989; 64(3_suppl):1057–8. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1989.64.3c.1057
[30]Hosseine F, Khayyer M. [Prediction of behavioral and decisional procrastination considering meta-cognition beliefs in university students (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry & Clinical Psychology. 2009; 15(3):265-73.
[1]Abolghasemi A, Najarian B. [Test anxiety, assessment and treatment (Persian)]. Psychological Research. 2000; 5(3-4):82-99.
[2]Latas M, Pantic M, Bradovic D. Analysis of test anxiety in medical students. Medicinski Pregled. 2010; 63(11-12):863-6. doi: 10.2298/mpns1012863l
[3]Brown LA, Forman EM, Herbert JD, Hoffman KL, Goetter EM. A randomized Controlled trial of acceptance-based behavior therapy and cognitive therapy for test anxiety: A pilot Study. Behavioural Modification. 2011; 35(1):31-53. doi: 10.1177/0145445510390930
[4]Schaefer A, Matthess H, Pfitzer G, Kohle K. [Mental health and performance of medical students with high and low test anxiety (German)]. PPmP - Psychotherapie · Psychosomatik · Medizinische Psychologie. 2007; 57(7):289-97. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-951974
[5]Pless A. Treatment of test anxiety: A computerized approach [PhD dissertation]. Michigan: Centeral Michigan University; 2010.
[6]Morris LW, Liebert RM. Effects of anxiety on timed and untimed intelligence tests: Another look. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1969; 33(2):240–4. doi: 10.1037/h0027164
[7]Spilberger CD. Preliminary professional manual for the Test Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, California: Consulting Psychologist Press; 1980.
[8]Nasri S, Shahrokhi M, Ebrahim Damavandi M. [The prediction of academic procrastination on perfectionism and test anxiety (Persian)]. Research in School and Virtual Learning. 2013; 1(1):26-37.
[9]Howell AJ, Watson DC. Procrastination: Associations with achievement goal orientation and learning strategies. Personality and Individual Differences. 2007; 43(1):167–78. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2006.11.017
[10]Kim KR, Seo EH. The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: A meta-analysis. Personality and Individual Differences. 2015; 82:26–33. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.02.038
[11]Ferrari JR, Ozer BU, Demir A. Chronic procrastination among Turkish adults: Exploring decisional, avoidant, and arousal styles. The Journal of Social Psychology. 2009; 149(3):302-08. doi: 10.3200/socp.149.3.302-308
[12]Sheykhi M, Fathabadi J, Heidari M. [The relations of anxiety, self-efficacy and perfectionism to dissertation procrastination (Persian)]. Developmental Psychology. 2013; 9(35):283-95.
[13]Solomon LJ, Rothblum ED. Academic procrastination: Frequency and cognitive behavioural correlates. Journal of Counselling Psychology. 1984; 31(4):503-9. doi: 10.1037//0022-0167.31.4.503
[14]Soysa CK, Weiss A. Mediating perceived parenting styles–test anxiety relationships: Academic procrastination and maladaptive perfectionism. Learning and Individual Differences. 2014; 34:77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2014.05.004
[15]Putwain D, Symes W. Perceived fear appeals and examination performance: Facilitating or debilitating outcomes? Learning and Individual Differences. 2011; 21(2):227–32. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2010.11.022
[16]Ferrari JR, Dovidio JF. Examining behavioral processes in indecision: Decisional Procrastination and decision- making style. Journal of Research in Personality. 2000; 34(1):127–37. doi: 10.1006/jrpe.1999.2247
[17]Walsh JJ, Ugumba-Agwunobi G. Individual differences in statistics anxiety: The roles of perfectionism, procrastination and trait anxiety. Personality and Individual Differences. 2002; 33(2):239–51. doi: 10.1016/s0191-8869(01)00148-9
[18]Gosselin P, Langlois F, Freeston MH, Ladouceur R, Laberge M, Lemay D. Cognitive variables related to worry among adolescents: Avoidance strategies and faulty beliefs about worry. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2007; 45(2):225–33. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2006.03.001
[19]Bassak-nejad S, Hooman F, Ghasemi-nejad MA. [The relationship between cognitive-behavioral avoidance coping styles with eating disorder among university students (Persian)]. Journal of Fundamentals of Mental Health. 2013; 14(56):278-85.
[20]Beesdo-Baum K, Jenjahn E, Höfler M, Lueken U, Becker ES, Hoyer J. Avoidance, safety behavior, and reassurance seeking in generalized anxiety disorder. Depression and Anxiety. 2012; 29(11):948‒57. doi: 10.1002/da.21955
[21]Moini N. [A study of relationship between post event processing and cognitive avoidance with social anxiety among students of Shahid Chamran university of Ahwaz (Persian)] [MSc. thesis]. Ahwaz: Shahid Chamran University of Ahwaz; 2010.
[22]Bassak Nejad S. The relationship between cognitive avoidance and pathological worry among university students. Paper presente at: 23rd Conference of EHPS. 15-19 September 2009; Pisa, Italy.
[23]Dickson KS, Ciesla JA. Reilly LC. Rumination, worry, cognitive avoidance, and behavioral avoidance: Examination of temporal effects. Behavior Therapy. 2012; 43(3):629–40. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2011.11.002
[24]Sexton, KA. Dugas MJ. The cognitive avoidance questionare: Vlidetion of the English translation. Journal of Anxiety Disorder. 2008; 22(3):355–70. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.04.005
[25]Gosselin P, Langlois F, Freeston MH, Ladouceur R, Dugas MJ, Pelletier O. [The Cognitive Avoidance Questionnaire(CAQ): Development and validation among adult and adolescent samples (French)]. Journal de The´rapie Comportementale et Cognitive 2002; 12(1):24–37.
[26]Bassak-nejad S, Moini N, Mehrabizadeh-Honarmand M. [The relationship between post event processing and cognitive avoidance with social anxiety among students (Persian)]. International Journal of Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 4(4): 335-40.
[27]Fridman I, Bendas-Jacob O. Measuring precieved test anxiety inadolescents: A self-report scale. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 1997; 57(6):1035–46. doi: 10.1177/0013164497057006012
[28]Lay CH. At last, my research article on procrastination. Journal of Research in Personality. 1986; 20(4):474–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-6566(86)90127-3
[29]Ferrari JR. Reliability of academic and dispositional measure of procrastination. Psychological Reports. 1989; 64(3_suppl):1057–8. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1989.64.3c.1057
[30]Hosseine F, Khayyer M. [Prediction of behavioral and decisional procrastination considering meta-cognition beliefs in university students (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry & Clinical Psychology. 2009; 15(3):265-73.
[31]Mann L. Decision-making questionnaire. Unpublished inventory. Adelaide: Flinders University; 1982.
[32]Spada MM, Hiou K, Nikcevic AV. Meta cognitions, emotions, and procrastination. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy. 2006; 20(3):319–26. doi: 10.1891/jcop.20.3.319
[33]McCown WG, Ferrari JR, Johnson J. Procrastination and task avoidance: Theory, research, and treatment. Berlin: Springer; 1995.
[34]Frost RO, Shows DL. The nature and measurement of compulsive indecisiveness. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 1993; 31(7):683–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(93)90121-a
[35]Zeisler L. Association between stress and decisional procrastination in parents of children with down syndrome during their developemental transitions [PhD dissertations]. South Orange, New Jersey: Seton Hall University; 2011.
[36]Vahedi SH, Farrokhi F, Gahramani F, Issazadegan A. The relationship between procrastination, Learning strategies and statistics anxiety among Iranian college student: A canonical correlation analysis. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences. 2012; 6(1):40-46.
[37]Rothblum ED, Solomon LJ, Murakami J. Affective, cognitive, and behavioral differences between high and low procrastinators. Journal of Counseling Psychology. 1986; 33(4):387–94. doi: 10.1037/0022-0167.33.4.387
[38]Onwuegbuzie AJ. Academic procrastination and statistics anxiety. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education. 2004; 29(1):3–19. doi: 10.1080/0260293042000160384
[39]Fiore N. The now habit: A strategic program for overcoming procrastination and enjoying guilt-free play. New York: Penguin Group; 1989.
[40]Endler NS, Parker JD. Multidimensional assessment of coping: A critical evaluation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1990; 58(5):844–54. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.58.5.844
[41]Balkis M, Duru E. The evaluation of the major characteristics and aspects of the procrastination in the framework of psychological counseling and guidance. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice 2007; 7(1):376-85.
[42]Chu AC, Chol JN. Rethinking procrastination: Positive effects of active procrastination behavior on attiudes and performance. Journal of Social Psychology. 2005; 145(3):245–64. doi: 10.3200/socp.145.3.245-264
[43]Lay CH. The relationship of procrastination and optimism to judgments of time to complete an essay and anticipation of setbacks. Journal of Social Behavior & Personality. 1988; 3(3):201-14.
[44]Sadeghi H. The study of relation between meta cognition beleifs and procrastination among students of Tabriz and Mohaghegh Ardabili Universities. Procedia - social and Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 30:287-91. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.10.057
[45]Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping. Berlin: Springer; 1984.
[32]Spada MM, Hiou K, Nikcevic AV. Meta cognitions, emotions, and procrastination. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy. 2006; 20(3):319–26. doi: 10.1891/jcop.20.3.319
[33]McCown WG, Ferrari JR, Johnson J. Procrastination and task avoidance: Theory, research, and treatment. Berlin: Springer; 1995.
[34]Frost RO, Shows DL. The nature and measurement of compulsive indecisiveness. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 1993; 31(7):683–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(93)90121-a
[35]Zeisler L. Association between stress and decisional procrastination in parents of children with down syndrome during their developemental transitions [PhD dissertations]. South Orange, New Jersey: Seton Hall University; 2011.
[36]Vahedi SH, Farrokhi F, Gahramani F, Issazadegan A. The relationship between procrastination, Learning strategies and statistics anxiety among Iranian college student: A canonical correlation analysis. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences. 2012; 6(1):40-46.
[37]Rothblum ED, Solomon LJ, Murakami J. Affective, cognitive, and behavioral differences between high and low procrastinators. Journal of Counseling Psychology. 1986; 33(4):387–94. doi: 10.1037/0022-0167.33.4.387
[38]Onwuegbuzie AJ. Academic procrastination and statistics anxiety. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education. 2004; 29(1):3–19. doi: 10.1080/0260293042000160384
[39]Fiore N. The now habit: A strategic program for overcoming procrastination and enjoying guilt-free play. New York: Penguin Group; 1989.
[40]Endler NS, Parker JD. Multidimensional assessment of coping: A critical evaluation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1990; 58(5):844–54. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.58.5.844
[41]Balkis M, Duru E. The evaluation of the major characteristics and aspects of the procrastination in the framework of psychological counseling and guidance. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice 2007; 7(1):376-85.
[42]Chu AC, Chol JN. Rethinking procrastination: Positive effects of active procrastination behavior on attiudes and performance. Journal of Social Psychology. 2005; 145(3):245–64. doi: 10.3200/socp.145.3.245-264
[43]Lay CH. The relationship of procrastination and optimism to judgments of time to complete an essay and anticipation of setbacks. Journal of Social Behavior & Personality. 1988; 3(3):201-14.
[44]Sadeghi H. The study of relation between meta cognition beleifs and procrastination among students of Tabriz and Mohaghegh Ardabili Universities. Procedia - social and Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 30:287-91. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.10.057
[45]Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping. Berlin: Springer; 1984.
Type of Study: Original Research |
Subject:
Psychiatry and Psychology
Received: 2016/09/18 | Accepted: 2017/04/15 | Published: 2018/01/1
Received: 2016/09/18 | Accepted: 2017/04/15 | Published: 2018/01/1
References
1. Abolghasemi A, Najarian B. [Test anxiety, assessment and treatment (Persian)]. Psychological Research. 2000; 5(3-4):82-99.
2. Latas M, Pantic M, Bradovic D. Analysis of test anxiety in medical students. Medicinski Pregled. 2010; 63(11-12):863-6. doi: 10.2298/mpns1012863l [DOI:10.2298/MPNS1012863L]
3. Brown LA, Forman EM, Herbert JD, Hoffman KL, Goetter EM. A randomized Controlled trial of acceptance-based behavior therapy and cognitive therapy for test anxiety: A pilot Study. Behavioural Modification. 2011; 35(1):31-53. doi: 10.1177/0145445510390930 [DOI:10.1177/0145445510390930]
4. Schaefer A, Matthess H, Pfitzer G, Kohle K. [Mental health and performance of medical students with high and low test anxiety (German)]. PPmP - Psy-chotherapie · Psychosomatik · Medizinische Psychologie. 2007; 57(7):289-97. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-951974 [DOI:10.1055/s-2006-951974]
5. Pless A. Treatment of test anxiety: A computerized approach [PhD dissertation]. Michigan: Centeral Michigan University; 2010.
6. Morris LW, Liebert RM. Effects of anxiety on timed and untimed intelligence tests: Another look. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1969; 33(2):240–4. doi: 10.1037/h0027164 [DOI:10.1037/h0027164]
7. Spilberger CD. Preliminary professional manual for the Test Anxiety Inventory. Palo Alto, California: Consulting Psychologist Press; 1980.
8. Nasri S, Shahrokhi M, Ebrahim Damavandi M. [The prediction of academic procrastination on perfectionism and test anxiety (Persian)]. Research in School and Virtual Learning. 2013; 1(1):26-37.
9. Howell AJ, Watson DC. Procrastination: Associations with achievement goal orientation and learning strategies. Personality and Individual Differences. 2007; 43(1):167–78. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2006.11.017 [DOI:10.1016/j.paid.2006.11.017]
10. Kim KR, Seo EH. The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: A meta-analysis. Personality and Individual Differences. 2015; 82:26–33. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.02.038 [DOI:10.1016/j.paid.2015.02.038]
11. Ferrari JR, Ozer BU, Demir A. Chronic procrastination among Turkish adults: Exploring decisional, avoidant, and arousal styles. The Journal of Social Psychology. 2009; 149(3):302-08. doi: 10.3200/socp.149.3.302-308 [DOI:10.3200/SOCP.149.3.302-308]
12. Sheykhi M, Fathabadi J, Heidari M. [The relations of anxiety, self-efficacy and perfectionism to dissertation procrastination (Persian)]. Developmental Psy-chology. 2013; 9(35):283-95.
13. Solomon LJ, Rothblum ED. Academic procrastination: Frequency and cognitive behavioural correlates. Journal of Counselling Psychology. 1984; 31(4):503-9. doi: 10.1037//0022-0167.31.4.503 [DOI:10.1037//0022-0167.31.4.503]
14. Soysa CK, Weiss A. Mediating perceived parenting styles–test anxiety relationships: Academic procrastination and maladaptive perfectionism. Learning and Individual Differences. 2014; 34:77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2014.05.004 [DOI:10.1016/j.lindif.2014.05.004]
15. Putwain D, Symes W. Perceived fear appeals and examination performance: Facilitating or debilitating outcomes? Learning and Individual Differences. 2011; 21(2):227–32. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2010.11.022 [DOI:10.1016/j.lindif.2010.11.022]
16. Ferrari JR, Dovidio JF. Examining behavioral processes in indecision: Decisional Procrastination and decision- making style. Journal of Research in Person-ality. 2000; 34(1):127–37. doi: 10.1006/jrpe.1999.2247 [DOI:10.1006/jrpe.1999.2247]
17. Walsh JJ, Ugumba-Agwunobi G. Individual differences in statistics anxiety: The roles of perfectionism, procrastination and trait anxiety. Personality and Individual Differences. 2002; 33(2):239–51. doi: 10.1016/s0191-8869(01)00148-9 [DOI:10.1016/S0191-8869(01)00148-9]
18. Gosselin P, Langlois F, Freeston MH, Ladouceur R, Laberge M, Lemay D. Cognitive variables related to worry among adolescents: Avoidance strategies and faulty beliefs about worry. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2007; 45(2):225–33. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2006.03.001 [DOI:10.1016/j.brat.2006.03.001]
19. Bassak-nejad S, Hooman F, Ghasemi-nejad MA. [The relationship between cognitive-behavioral avoidance coping styles with eating disorder among uni-versity students (Persian)]. Journal of Fundamentals of Mental Health. 2013; 14(56):278-85.
20. Beesdo-Baum K, Jenjahn E, Höfler M, Lueken U, Becker ES, Hoyer J. Avoidance, safety behavior, and reassurance seeking in generalized anxiety disorder. Depression and Anxiety. 2012; 29(11):948‒57. doi: 10.1002/da.21955 [DOI:10.1002/da.21955]
21. Moini N. [A study of relationship between post event processing and cognitive avoidance with social anxiety among students of Shahid Chamran universi-ty of Ahwaz (Persian)] [MSc. thesis]. Ahwaz: Shahid Chamran University of Ahwaz; 2010.
22. Bassak Nejad S. The relationship between cognitive avoidance and pathological worry among university students. Paper presente at: 23rd Conference of EHPS. 15-19 September 2009; Pisa, Italy.
23. Dickson KS, Ciesla JA. Reilly LC. Rumination, worry, cognitive avoidance, and behavioral avoidance: Examination of temporal effects. Behavior Therapy. 2012; 43(3):629–40. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2011.11.002 [DOI:10.1016/j.beth.2011.11.002]
24. Sexton, KA. Dugas MJ. The cognitive avoidance questionare: Vlidetion of the English translation. Journal of Anxiety Disorder. 2008; 22(3):355–70. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.04.005 [DOI:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.04.005]
25. Gosselin P, Langlois F, Freeston MH, Ladouceur R, Dugas MJ, Pelletier O. [The Cognitive Avoidance Questionnaire(CAQ): Development and validation among adult and adolescent samples (French)]. Journal de The’rapie Comportementale et Cognitive 2002; 12(1):24–37.
26. Bassak-nejad S, Moini N, Mehrabizadeh-Honarmand M. [The relationship between post event processing and cognitive avoidance with social anxiety among students (Persian)]. International Journal of Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 4(4): 335-40.
27. Fridman I, Bendas-Jacob O. Measuring precieved test anxiety inadolescents: A self-report scale. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 1997; 57(6):1035–46. doi: 10.1177/0013164497057006012 [DOI:10.1177/0013164497057006012]
28. Lay CH. At last, my research article on procrastination. Journal of Research in Personality. 1986; 20(4):474–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-6566(86)90127-3 [DOI:10.1016/0092-6566(86)90127-3]
29. Ferrari JR. Reliability of academic and dispositional measure of procrastination. Psychological Reports. 1989; 64(3_suppl):1057–8. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1989.64.3c.1057 [DOI:10.2466/pr0.1989.64.3c.1057]
30. Hosseine F, Khayyer M. [Prediction of behavioral and decisional procrastination considering meta-cognition beliefs in university students (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry & Clinical Psychology. 2009; 15(3):265-73.
31. Mann L. Decision-making questionnaire. Unpublished inventory. Adelaide: Flinders University; 1982.
32. Spada MM, Hiou K, Nikcevic AV. Meta cognitions, emotions, and procrastination. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy. 2006; 20(3):319–26. doi: 10.1891/jcop.20.3.319 [DOI:10.1891/jcop.20.3.319]
33. McCown WG, Ferrari JR, Johnson J. Procrastination and task avoidance: Theory, research, and treatment. Berlin: Springer; 1995.
34. Frost RO, Shows DL. The nature and measurement of compulsive indecisiveness. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 1993; 31(7):683–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(93)90121-a [DOI:10.1016/0005-7967(93)90121-A]
35. Zeisler L. Association between stress and decisional procrastination in parents of children with down syndrome during their developemental transitions [PhD dissertations]. South Orange, New Jersey: Seton Hall University; 2011. [PMCID]
36. Vahedi SH, Farrokhi F, Gahramani F, Issazadegan A. The relationship between procrastination, Learning strategies and statistics anxiety among Iranian college student: A canonical correlation analysis. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences. 2012; 6(1):40-46. [PMID] [PMCID]
37. Rothblum ED, Solomon LJ, Murakami J. Affective, cognitive, and behavioral differences between high and low procrastinators. Journal of Counseling Psy-chology. 1986; 33(4):387–94. doi: 10.1037/0022-0167.33.4.387 [DOI:10.1037/0022-0167.33.4.387]
38. Onwuegbuzie AJ. Academic procrastination and statistics anxiety. Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education. 2004; 29(1):3–19. doi: 10.1080/0260293042000160384 [DOI:10.1080/0260293042000160384]
39. Fiore N. The now habit: A strategic program for overcoming procrastination and enjoying guilt-free play. New York: Penguin Group; 1989. [PMCID]
40. Endler NS, Parker JD. Multidimensional assessment of coping: A critical evaluation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1990; 58(5):844–54. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.58.5.844 [DOI:10.1037/0022-3514.58.5.844]
41. Balkis M, Duru E. The evaluation of the major characteristics and aspects of the procrastination in the framework of psychological counseling and guid-ance. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice 2007; 7(1):376-85.
42. Chu AC, Chol JN. Rethinking procrastination: Positive effects of active procrastination behavior on attiudes and performance. Journal of Social Psychology. 2005; 145(3):245–64. doi: 10.3200/socp.145.3.245-264 [DOI:10.3200/SOCP.145.3.245-264]
43. Lay CH. The relationship of procrastination and optimism to judgments of time to complete an essay and anticipation of setbacks. Journal of Social Behav-ior & Personality. 1988; 3(3):201-14.
44. Sadeghi H. The study of relation between meta cognition beleifs and procrastination among students of Tabriz and Mohaghegh Ardabili Universities. Pro-cedia - social and Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 30:287-91. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.10.057 [DOI:10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.10.057]
45. Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping. Berlin: Springer; 1984.
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |