Sun, Aug 31, 2025
| فارسی
Volume 23, Issue 2 (Summer 2017)
IJPCP 2017, 23(2): 208-217 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
pourasghar M, Najafi K, Tirgari A, Yazdani J, Falaki M, Salehi F. Investigating Employees’ and Health Care Practitioners’ Communication Skills. IJPCP 2017; 23 (2) :208-217
URL: http://ijpcp.iums.ac.ir/article-1-2454-en.html
URL: http://ijpcp.iums.ac.ir/article-1-2454-en.html
Mehdi Pourasghar1 
 , Kyumars Najafi2
, Kyumars Najafi2 
 , Abdolhakim Tirgari1
, Abdolhakim Tirgari1 
 , Jamshid Yazdani3
, Jamshid Yazdani3 
 , Mozhgan Falaki4
, Mozhgan Falaki4 
 , Fariba Salehi5
, Fariba Salehi5 


 , Kyumars Najafi2
, Kyumars Najafi2 
 , Abdolhakim Tirgari1
, Abdolhakim Tirgari1 
 , Jamshid Yazdani3
, Jamshid Yazdani3 
 , Mozhgan Falaki4
, Mozhgan Falaki4 
 , Fariba Salehi5
, Fariba Salehi5 

1- Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Research Center, School of Medicine, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences
2- Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Guilan University of Medical Sciences
3- Department of Biostatistics & Epidemiology, Faculty of Health Sciences, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences
4- Department of Midwifery, Nasibe Nursing and Midwifery School of Sari, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences
5- Department of Midwifery, Nasibe Nursing and Midwifery School of Sari, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences ,E-mail: salehy.fariba@yahoo.com
2- Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Guilan University of Medical Sciences
3- Department of Biostatistics & Epidemiology, Faculty of Health Sciences, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences
4- Department of Midwifery, Nasibe Nursing and Midwifery School of Sari, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences
5- Department of Midwifery, Nasibe Nursing and Midwifery School of Sari, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences ,
Full-Text [PDF 2276 kb]
(3976 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (8045 Views)
Full-Text: (7464 Views)
Extended Abstract
1. Introduction
Communication skill is one of the essential skills of human life. According to many scholars and psychologists, communication skill is one of the main concern and challenging factor in human life for being successful. The Importance of Communication Skills in social life is so much that some thinkers know the basis of human growth, personal injury, and human progress in the process of communication. Studies have showed that many employees consider the role of communication skills in their job success to be more important than specific technical skills. Managers and staff who are skilled in communication are faced with fewer problems, make fewer errors, spend fewer resources, and also handle their opponents more efficiently. Communication skills are recognized as an important component of medical and nursing care. Effective communication has always been raised as the basis of quality of care services. Ability to communicate with colleagues, patients and others forms the basis of clinical skills required to provide ideal medical care and the core of the optimal medical activity. Establishing therapeutic communication is considered as the most basic step in the field of treatment in a way that many scholars believe that establishing therapeutic communication has an essential contribution to the success of the treatment. This study has been conducted with the aim of determining the status of communication skills and its related factors in health care workers and employees.
2. Method
This study uses survey and descriptive-analytical design. The sample size was 409, consisting of staff and workers of the Zare’ psychiatric and burn hospital of Sari City in 2015. It was carried out by census method.
Data collection method was based on unnamed questionnaires. Measurement tool in this study was an unnamed questionnaire that was divided into two sections: 1) Demographic characteristics; and 2) Standard questionnaire for communication skills. This questionnaire has been excerpted from the revised version of Inventory of Communication Skills. This questionnaire is standardized in Iran, and its validity and reliability have been determined. The credibility of this questionnaire has been reported to be 0.71 and 0.69 using the Cronbach’s Alpha Method and Split Half method. This test includes 34 questions with 5 sub-scales of ability to receive or understand verbal and nonverbal messages, ordering the emotions, listening skill, insight into the process of communication, and decisiveness in communication.
After collecting questionnaires, data were entered into SPSS statistical software version 18, and data analysis was carried out using the t-test parametric test in relation to the comparison of the means of data in an independent population for means such as age, gender, level of education, work experience, position and workplace. Based on the nature of the variables in terms of being quantitative or qualitative and according to the goals and assumptions of the study, ANOVA test was used to check the relationship between data.
3. Results
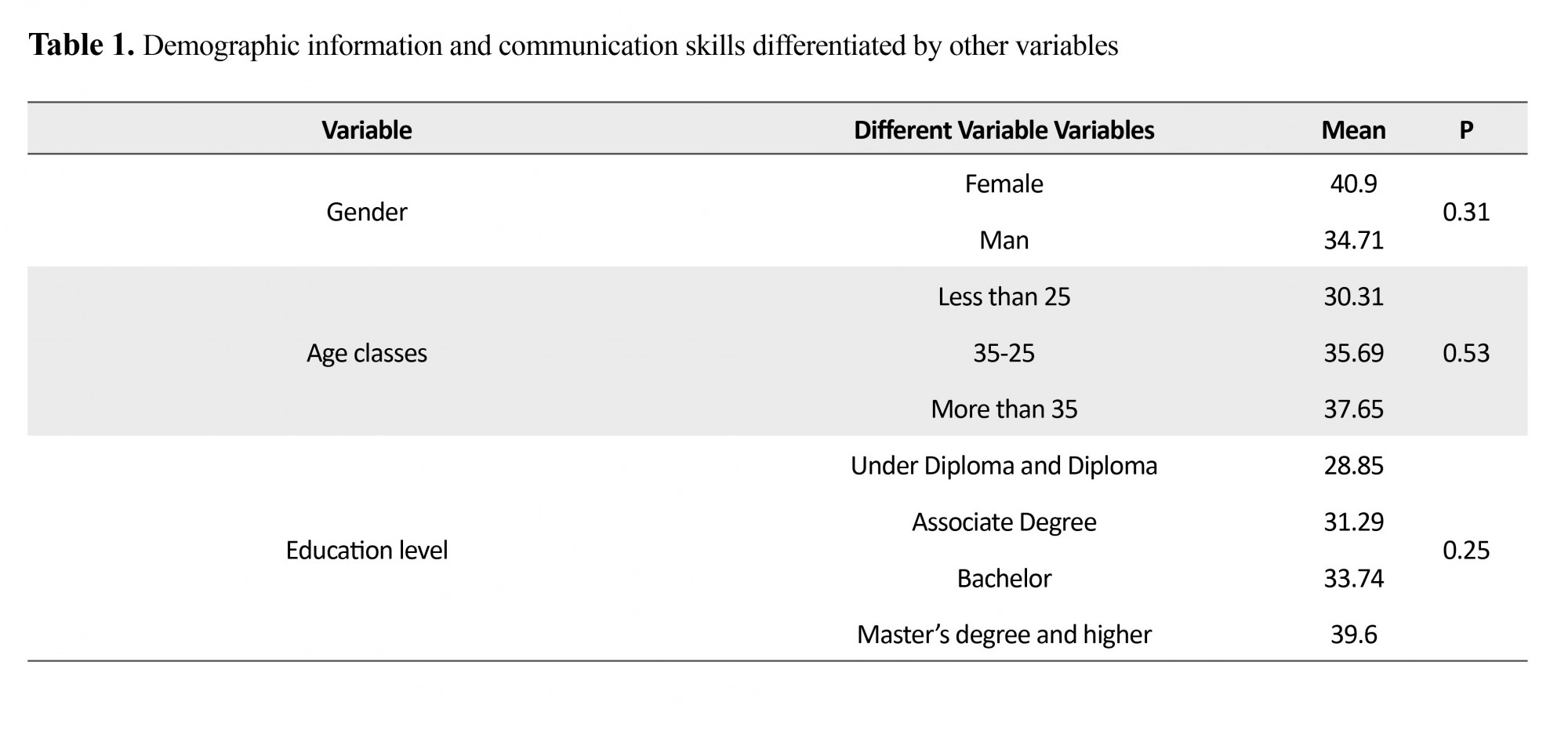
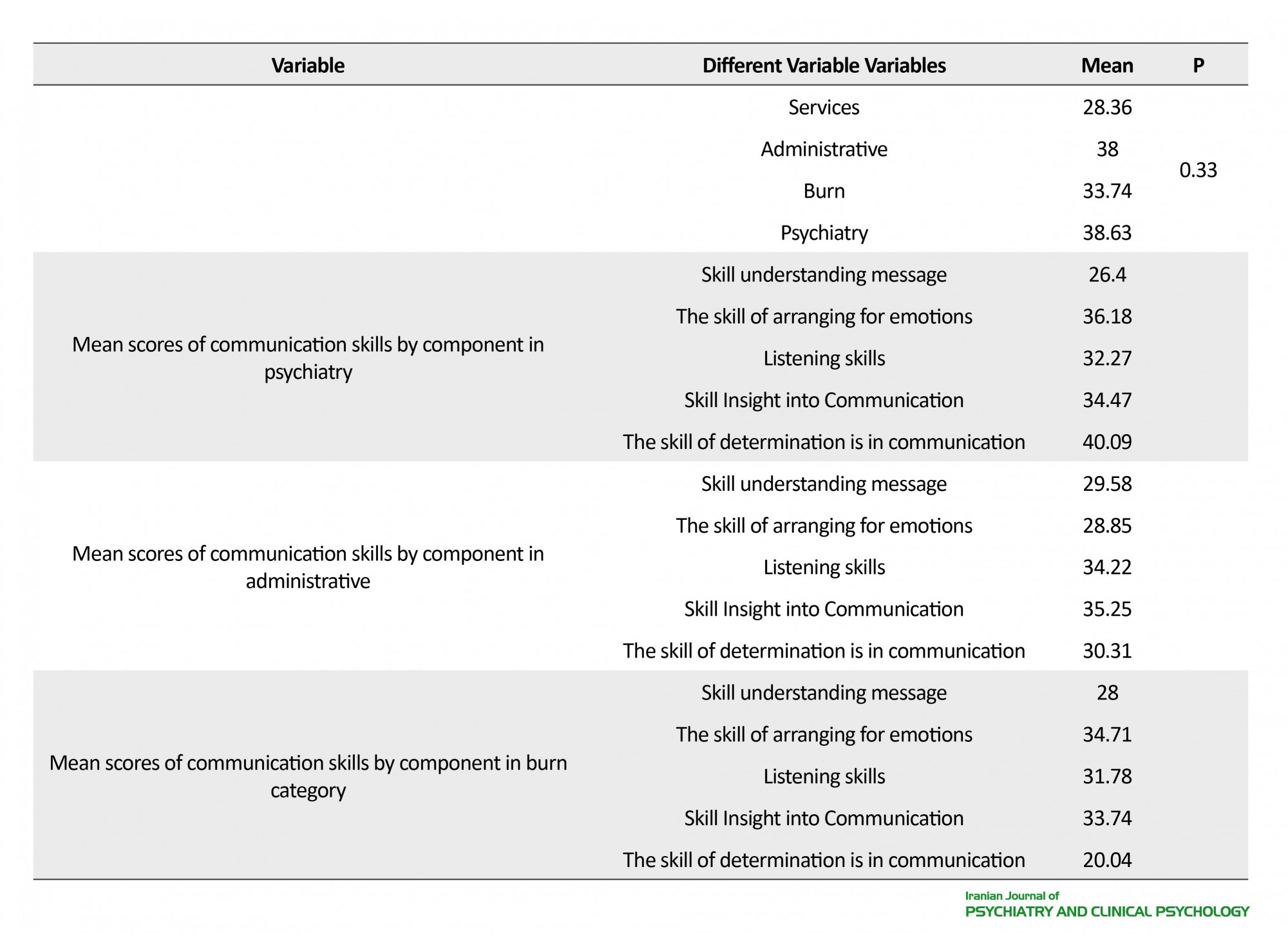
In the present study, the average age of participants was 34.9 years. Of the total 409, 198 participants (48.4%) were women and 211(51.6%) were men. It was also found that 147 participants had under-diploma education level, 47 were undergraduate, 195 had Bachelor Degree, and 20 had Master’s Degree and higher. The average work experience was 4.7±1.9 years; based on the place of service, 21.76% of the participants worked in the clinical department of psychiatry, 42.78% in the burned-healing section, 15.5% in the administrative department, and 29.20% were working in the service sector. There were 159 officially recruited participants, 212 contracted staff, and 38 were termed employees. In data analysis, the average score of communication skills was 154, which was at a desirable level. Average total points earned under the sub-scales were separately documented as follows: Skill of understanding message was 31.21, the ordering skill of excitement was 31.73, listening skill 31.63, insight into communication 31.17, and decisiveness was 31.34. Average rating of communication skills was 40.90 and 34.71 in women and men, respectively. Although the score of communication skills varies among men and women, but this difference was not significant (P=0.53).
4. Discussion
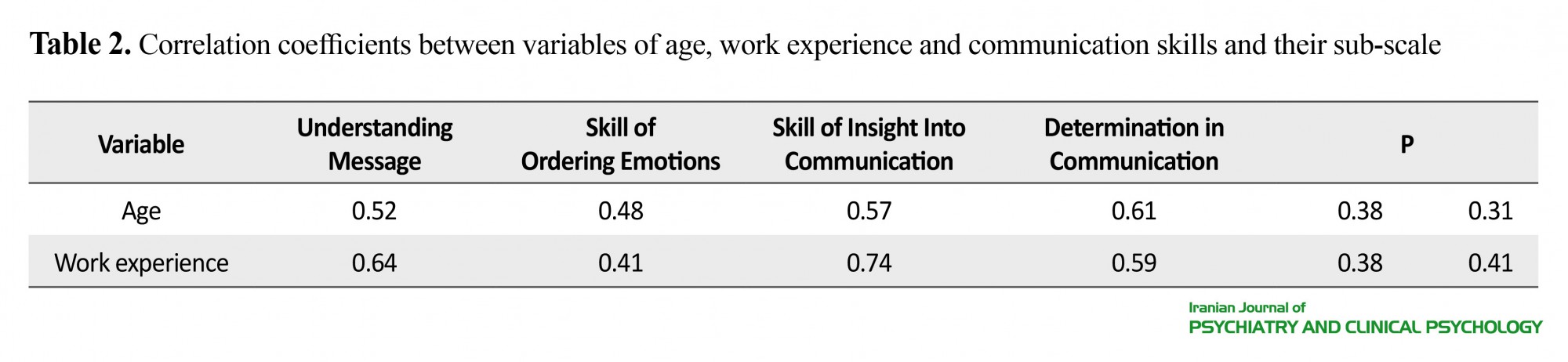
Based on the results of this study, there is a significant relationship between age, the level of education, and communication skills (P=0.31), (P=0.31), (Table 1). Table 2 shows a significant correlation between variables of age and work history with the components of communication skills.
1. Introduction
Communication skill is one of the essential skills of human life. According to many scholars and psychologists, communication skill is one of the main concern and challenging factor in human life for being successful. The Importance of Communication Skills in social life is so much that some thinkers know the basis of human growth, personal injury, and human progress in the process of communication. Studies have showed that many employees consider the role of communication skills in their job success to be more important than specific technical skills. Managers and staff who are skilled in communication are faced with fewer problems, make fewer errors, spend fewer resources, and also handle their opponents more efficiently. Communication skills are recognized as an important component of medical and nursing care. Effective communication has always been raised as the basis of quality of care services. Ability to communicate with colleagues, patients and others forms the basis of clinical skills required to provide ideal medical care and the core of the optimal medical activity. Establishing therapeutic communication is considered as the most basic step in the field of treatment in a way that many scholars believe that establishing therapeutic communication has an essential contribution to the success of the treatment. This study has been conducted with the aim of determining the status of communication skills and its related factors in health care workers and employees.
2. Method
This study uses survey and descriptive-analytical design. The sample size was 409, consisting of staff and workers of the Zare’ psychiatric and burn hospital of Sari City in 2015. It was carried out by census method.
Data collection method was based on unnamed questionnaires. Measurement tool in this study was an unnamed questionnaire that was divided into two sections: 1) Demographic characteristics; and 2) Standard questionnaire for communication skills. This questionnaire has been excerpted from the revised version of Inventory of Communication Skills. This questionnaire is standardized in Iran, and its validity and reliability have been determined. The credibility of this questionnaire has been reported to be 0.71 and 0.69 using the Cronbach’s Alpha Method and Split Half method. This test includes 34 questions with 5 sub-scales of ability to receive or understand verbal and nonverbal messages, ordering the emotions, listening skill, insight into the process of communication, and decisiveness in communication.
After collecting questionnaires, data were entered into SPSS statistical software version 18, and data analysis was carried out using the t-test parametric test in relation to the comparison of the means of data in an independent population for means such as age, gender, level of education, work experience, position and workplace. Based on the nature of the variables in terms of being quantitative or qualitative and according to the goals and assumptions of the study, ANOVA test was used to check the relationship between data.
3. Results
In the present study, the average age of participants was 34.9 years. Of the total 409, 198 participants (48.4%) were women and 211(51.6%) were men. It was also found that 147 participants had under-diploma education level, 47 were undergraduate, 195 had Bachelor Degree, and 20 had Master’s Degree and higher. The average work experience was 4.7±1.9 years; based on the place of service, 21.76% of the participants worked in the clinical department of psychiatry, 42.78% in the burned-healing section, 15.5% in the administrative department, and 29.20% were working in the service sector. There were 159 officially recruited participants, 212 contracted staff, and 38 were termed employees. In data analysis, the average score of communication skills was 154, which was at a desirable level. Average total points earned under the sub-scales were separately documented as follows: Skill of understanding message was 31.21, the ordering skill of excitement was 31.73, listening skill 31.63, insight into communication 31.17, and decisiveness was 31.34. Average rating of communication skills was 40.90 and 34.71 in women and men, respectively. Although the score of communication skills varies among men and women, but this difference was not significant (P=0.53).
4. Discussion
Based on the results of this study, there is a significant relationship between age, the level of education, and communication skills (P=0.31), (P=0.31), (Table 1). Table 2 shows a significant correlation between variables of age and work history with the components of communication skills.
Acknowledgments
Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences has financially supported the present paper.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences has financially supported the present paper.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
References
- Namdar H, Rahmani A, Ebrahimi H. [The effect of a skill-training model on nursing students’ skills in communicating with mental patients (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2009; 8(2):323-332.
- Zeyghami Mohammadi Sh, Haghighi S. [The association between nurses’ communication skills and nurse-physician relationship and collaboration in Alborz hospital of Karaj in 2008 (Persian)]. Medical Sciences. 2009; 19(2):121-127.
- Mohr J, Spekman R. Characteristics of partnership success: Partnership attributes, communication behavior, and conflict resolution techniques. Strategic Management Journal. 1994; 15(2):135–52. doi: 10.1002/smj.4250150205
- Greenhalgh T, Robert G, Macfarlane F, Bate P, Kyriakidou O. Diffusion of innovations in service organizations: systematic review and recommendations. The Milbank Quarterly. 2004; 82(4):581–629. doi: 10.1111/j.0887-378x.2004.00325.x
- Griffin RW, Moorhead G. Organizational behavior: Managing people and organizations. Kentucky: South-Western College Pub; 2016.
- Rosemann M, Vom Brocke J. The six core elements of business process management. In: Rosemann M, editor. Hand Book on Business Process Management. Berlin: Springer; 2015.
- Buoziute-Rafanaviciene S, Pudziene A, Turauskas L. Relation between the attributes of executive successor and organizational performance. Engineering Economics. 2009; 62(2):65-74.
- Austin EW, Pinkleton BE. Strategic public relations management: Planning and managing effective communication campaigns. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2015.
- Arnold EC, Boggs KU. Interpersonal relationships: Professional communication skills for nurses. Amsterdam: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2015.
- White RO, Eden S, Wallston KA, Kripalani S, Barto S, Shintani A, et al. Health communication, self-care, and treatment satisfaction among low-income diabetes patients in a public health setting. Patient Education and Counseling. 2015; 98(2):144-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2014.10.019
- O’Halloran R,Worrall L, Hickson L. Environmental factors that influence communication between patients and their healthcare providers in acute hospital stroke units: An observational study. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorder. 2011; 46(1):30-47. doi: 10.3109/13682821003660380
- Humphris G.M. Improving health professionals’ communication skills: A major global endeavour. Patient Education and Counseling. 2015; 98(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2014.11.001
- Mehrshadian M, Valaiee N, Abzan S, Ramezani G, Farhangi A, Dadgaran M, et al. Communication skills of dentist faculty members of Islamic Azad university based on a student survey and its relation with faculties evaluation by students. Journal of Medical Education. 2007;11(3-4):91-95.
- Chant S, Jenkinson T, Randle J, Russell G. Communication skills: Some problems in nursing education and practice. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2002; 11(1):12-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2702.2002.00553.x
- Khatami SA, Sefzadeh S. [Communication skills of medical interns of Qazvin UMS (Persian)]. Journal of Qazvin University of Medical Sciences. 2007; 11(3):79-81.
- Hamidi Y, Barati M. Communication skills of heads of departments: verbal, listening, and feedback skills. Journal of Research in Health Sciences. 2011; 11(2):57-67.
- Saffari M, Shojaeizadeh D. [Health communication (Persian)]. 1st edition. Tehran: Asare Sobhan Publisher; 2010.
- Keyvani S. [Reviews and interactive communication skills in patients over 18 years of mental jump (Persian)] [MSc. thesis]. Tehran: University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation; 2001.
- Farber BA. Introduction: Understanding and treating burnout in a changing culture. Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2000; 56(5):589-594. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4679(200005)56:5<589::aid-jclp1>3.0.co;2-s
- Rhezaii Sh, Hosseini AM, Fallahi M. [Evaluating impact of communication skills training on level of job stress among nursing personnel working at rehabilitation centers in cities: Ray- Tehran-Shemiranat (Persian)]. Tehran University of Medical Sciences. 2006; 64(1):21-26.
- Brown JB, Boles M, Mullooly JP, Levinson W. Effect of clinician communication skills training on patient satisfaction. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1999; 131(11):822-829. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-131-11-199912070-00004
- Zamani AR, Shams B, Farajzadegan Z, Tabaeian SM. [The viewpoints of clinical faculty members about teaching communication skills to medical students (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2003; 3(1):45-51.
- Barati M, Afsar A, Ahmadpanah M. [Assessment of communication skills level among health care practitioners (Persian)]. Scientific Journal of Hamedan University of Medical Sciences and Health Services. 2012; 19(1):62-69.
- Pakgohar M, Rahimikian F, Mehran A, Mohammadi T. [Quality assessment of family planning counselling in health and treatment centers, affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Persian)]. Hayat. 2002; 8(2):62-71.
- Baghiani Moghadam M, Momayezi M. [Communication skills of department heads in Shahid Sadoughi university of medical sciences (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2012; 12(6):448-457
- Sabzevari S, Soltani Arabshahi K, Shekarabi R, Koohpayehzadeh J. [Nursing students’ communication with patients in hospitals affiliated to Kerman university of medical sciences (Persian)].Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2006; 6(1):43-49.
- Hosseinchari M, Delavarpour MA. Do shy people lack communication skills? Developmental Psychology. 2007; 3(10):123-135.
- Salimi M, Peyman H, Sadeghifar J, Toloui Rakhshan S, Alizadeh M, Yamani N. [Assessment of interpersonal communication skills and associated factors among students of allied medicine school in Tehran university of medical sciences (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2013; 12(12):895-902
- Kebriae A, Akbari F, Hosseini M, Eftekhar Ardabilli H, Pour Reza A. [Survey on Quality gap in primary health care in Kashan health centers (Persian)]. Journal of Ghazvin University of Medical Sciences. 2004; 31:82-88.
Type of Study: Original Research |
Subject:
Psychiatry and Psychology
Received: 2016/02/16 | Accepted: 2017/02/22 | Published: 2017/07/1
Received: 2016/02/16 | Accepted: 2017/02/22 | Published: 2017/07/1
References
1. Namdar H, Rahmani A, Ebrahimi H. [The effect of a skill-training model on nursing students' skills in communicating with mental patients (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2009; 8(2):323-332.
2. Zeyghami Mohammadi Sh, Haghighi S. [The association between nurses' communication skills and nurse-physician relationship and collaboration in Alborz hospital of Karaj in 2008 (Persian)]. Medical Sciences. 2009; 19(2):121-127.
3. Mohr J, Spekman R. Characteristics of partnership success: Partnership attributes, communication behavior, and conflict resolution techniques. Strategic Management Journal. 1994; 15(2):135–52. doi: 10.1002/smj.4250150205 [DOI:10.1002/smj.4250150205]
4. Greenhalgh T, Robert G, Macfarlane F, Bate P, Kyriakidou O. Diffusion of innovations in service organizations: systematic review and recommendations. The Milbank Quarterly. 2004; 82(4):581–629. doi: 10.1111/j.0887-378x.2004.00325.x [DOI:10.1111/j.0887-378X.2004.00325.x]
5. Griffin RW, Moorhead G. Organizational behavior: Managing people and organizations. Kentucky: South-Western College Pub; 2016.
6. Rosemann M, Vom Brocke J. The six core elements of business process management. In: Rosemann M, editor. Hand Book on Business Process Management. Berlin: Springer; 2015. [DOI:10.1007/978-3-642-45100-3_5]
7. Buoziute-Rafanaviciene S, Pudziene A, Turauskas L. Relation between the attributes of executive successor and organizational performance. Engineering Economics. 2009; 62(2):65-74.
8. Austin EW, Pinkleton BE. Strategic public relations management: Planning and managing effective communication campaigns. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2015.
9. Arnold EC, Boggs KU. Interpersonal relationships: Professional communication skills for nurses. Amsterdam: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2015.
10. White RO, Eden S, Wallston KA, Kripalani S, Barto S, Shintani A, et al. Health communication, self-care, and treatment satisfaction among low-income diabetes patients in a public health setting. Patient Education and Counseling. 2015; 98(2):144-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2014.10.019 [DOI:10.1016/j.pec.2014.10.019]
11. O'Halloran R,Worrall L, Hickson L. Environmental factors that influence communication between patients and their healthcare providers in acute hospital stroke units: An observational study. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorder. 2011; 46(1):30-47. doi: 10.3109/13682821003660380 [DOI:10.3109/13682821003660380]
12. Humphris G.M. Improving health professionals' communication skills: A major global endeavour. Patient Education and Counseling. 2015; 98(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2014.11.001 [DOI:10.1016/j.pec.2014.11.001]
13. Mehrshadian M, Valaiee N, Abzan S, Ramezani G, Farhangi A, Dadgaran M, et al. Communication skills of dentist faculty members of Islamic Azad university based on a student survey and its relation with faculties evaluation by students. Journal of Medical Education. 2007;11(3-4):91-95.
14. Chant S, Jenkinson T, Randle J, Russell G. Communication skills: Some problems in nursing education and practice. Journal of Clinical Nursing. 2002; 11(1):12-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2702.2002.00553.x [DOI:10.1046/j.1365-2702.2002.00553.x]
15. Khatami SA, Sefzadeh S. [Communication skills of medical interns of Qazvin UMS (Persian)]. Journal of Qazvin University of Medical Sciences. 2007; 11(3):79-81.
16. Hamidi Y, Barati M. Communication skills of heads of departments: verbal, listening, and feedback skills. Journal of Research in Health Sciences. 2011; 11(2):57-67.
17. Saffari M, Shojaeizadeh D. [Health communication (Persian)]. 1st edition. Tehran: Asare Sobhan Publisher; 2010.
18. Keyvani S. [Reviews and interactive communication skills in patients over 18 years of mental jump (Persian)] [MSc. thesis]. Tehran: University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation; 2001.
19. Farber BA. Introduction: Understanding and treating burnout in a changing culture. Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2000; 56(5):589-594. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4679(200005)56:5<589::aid-jclp1>3.0.co;2-s
https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4679(200005)56:5<589::AID-JCLP1>3.0.CO;2-S [DOI:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4679(200005)56:53.0.CO;2-S]
20. Rhezaii Sh, Hosseini AM, Fallahi M. [Evaluating impact of communication skills training on level of job stress among nursing personnel working at rehabilitation centers in cities: Ray- Tehran-Shemiranat (Persian)]. Tehran University of Medical Sciences. 2006; 64(1):21-26.
21. Brown JB, Boles M, Mullooly JP, Levinson W. Effect of clinician communication skills training on patient satisfaction. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1999; 131(11):822-829. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-131-11-199912070-00004 [DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-131-11-199912070-00004]
22. Zamani AR, Shams B, Farajzadegan Z, Tabaeian SM. [The viewpoints of clinical faculty members about teaching communication skills to medical students (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2003; 3(1):45-51.
23. Barati M, Afsar A, Ahmadpanah M. [Assessment of communication skills level among health care practitioners (Persian)]. Scientific Journal of Hamedan University of Medical Sciences and Health Services. 2012; 19(1):62-69.
24. Pakgohar M, Rahimikian F, Mehran A, Mohammadi T. [Quality assessment of family planning counselling in health and treatment centers, affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Persian)]. Hayat. 2002; 8(2):62-71.
25. Baghiani Moghadam M, Momayezi M. [Communication skills of department heads in Shahid Sadoughi university of medical sciences (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2012; 12(6):448-457
26. Sabzevari S, Soltani Arabshahi K, Shekarabi R, Koohpayehzadeh J. [Nursing students' communication with patients in hospitals affiliated to Kerman university of medical sciences (Persian)].Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2006; 6(1):43-49.
27. Hosseinchari M, Delavarpour MA. Do shy people lack communication skills? Developmental Psychology. 2007; 3(10):123-135.
28. Salimi M, Peyman H, Sadeghifar J, Toloui Rakhshan S, Alizadeh M, Yamani N. [Assessment of interpersonal communication skills and associated factors among students of allied medicine school in Tehran university of medical sciences (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2013; 12(12):895-902
29. Kebriae A, Akbari F, Hosseini M, Eftekhar Ardabilli H, Pour Reza A. [Survey on Quality gap in primary health care in Kashan health centers (Persian)]. Journal of Ghazvin University of Medical Sciences. 2004; 31:82-88.
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |